Erlanger Dermatology
979 East 3rd Street
Suite A-445
Chattanooga, TN 37403
423-778-5693
Mon – Fri, 8AM – 4PM
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a condition where the cells in the skin begin to grow out of control, and can potentially spread to other parts of the body.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
Most skin cancers develop on skin exposed to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. However, it may also occur on areas of your skin not typically exposed to sunlight.
What Are the Main Types of Skin Cancer?
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
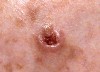
Basal cell carcinoma almost never spreads to the lymph nodes or internal organs, except under rare circumstances. However, it can invade and destroy the immediately surrounding tissue and cause deformity if left unchecked.
Treatment for basal cell cancer generally includes prescription creams or surgery to remove the cancer.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
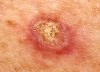
Squamous cell carcinoma can occasionally spread into the lymph nodes and internal organs. This most often occurs with large aggressive squamous cell carcinomas or rapidly growing tumors on the ears, scalp, lips or genitalia. An increased risk of spread is also seen in patients that area immunosuppressed, such as organ transplant patients, or those with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), or in tumors that have recurred after previous treatment.
Treatment for squamous cell carcinoma varies depending on the severity and specifics of each case. Treatment may involve surgery and sometimes chemotherapy and radiation.
Melanoma
Melanomas can develop anywhere on the skin, but are often found on the chest, back, abdomen, neck or head of men and on the arms and legs of women. People who have dark skin pigmentation have a lower risk of developing melanoma on the common sites mentioned above however, melanomas can occur on the palms of their hands, the soles of their feet and their nail beds.
Melanomas can also occur in other areas of the body such as the eyes, mouth, genitals, and anal area, but those cases are rare. Women should be sure their vaginal and cervix areas are examined for skin changes or new moles during their yearly OB/GYN examination.
Treatment for melanoma will vary depending on the severity of your case. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, medications, or in some cases chemotherapy.
Do a Monthly Skin Self-Exam
Because early detection of skin cancer is important for successful treatment, be sure to conduct a monthly skin self-exam and tell your doctor about any changes or new spots on your skin. You should also tell your doctor about any growths that look different than the rest of your moles. During your monthly skin self-exam, be mindful of the "A-B-C-D-E Rule" for early detection of melanoma.
Mohs Surgery for Skin Cancer
Mohs surgery is a precise surgical technique for treating skin cancer. This state-of-the-art procedure carefully removes cancerous skin cells layer by layer. Learn More

